Summery
Scenario-type planning is a designed plan to show what the
future will look like and how the business environment will develop and improve
in light of that future. (Mariton, 2016b) Fig 1 shows a quick view of how
scenario-type planning works. Scenario-type planning is the essential tool to
find uncertainties and different realities of the future of business. In other
words, scenario-type planning is to "way to assert control over an
uncertain world by identifying assumptions about the future." (Rami, et.,
2020b) So, what happens when there is no scenario-type planning on the table is
the purpose of this article. This article will answer some critical questions
and concerns, including how scenario-type planning supports the planning and
innovation for change (CTU, 2022). This article also has some thoughts about
how we will use scenario-type planning for future innovation efforts and how it
for the social impacts of changes. (CTU, 2022)
Scenario-type planning
Scenario-type (Scenario-based) planning is not some
assumptions about the future. It is "refining forecasts and explaining
differences against initial budget. The company just refers to the relevant
scenario and focuses on achieving its objectives." Scenario-type analysis
has several types, including Quantitative scenario-type planning (QNS),
Quantitative simulation modeling (SM), and Strategic management
scenarios-types. (Rami, 2020b)
Qualitative scenario-type planning (QLS)
QLS is the most common type of scenario planning, and it
focuses on organizations with actual data and analysis and relies on the
existing historical/experimental data. For example, NPS conducted a QLS
analysis from the Global Business Network (GBN) data to predict the future of
climate changes in park planning in 2009. (Symstad, 2017, p. 7)
Seventeen climate experts were the initial team to use a
qualitative scenarios (QLSs) method with a "nested" approach.
(Symstad, 2017) Their primary vital inputs were a table of projections,
including nine climate variables, existing data on climate influences on WCNP's
natural resources and ecosystems, and a list of climate-sensitive items.
(Symstad, 2017) The team found "Drought Severity" and "Precipitation
Patterns" with significant uncertainty in the "direction or magnitude
of change and potential impact on natural resources" (Symstad, 2017) in
the future.
Quantitative simulation modeling (SM)
Quantitative scenario-type analyses are "financial
models that allow for the presentation of best- and worst-case versions of the
model outputs" (Rami, 2020b). It is the best approach for annual business
forecasts. For example, on the same above research with QLS, the team of
researchers in NPS conducted a quantitative scenario planning to understand the
impact of ecosystems dynamics on climate change interacting with management
interventions. (Symstad, 2017, p. 8) The first step of this approach was a
"meeting between the science team and WCNP managers to exchange
information, align expectations with model capabilities, and jointly determine
the focal questions to address with the simulations." (Symstad, 2017, p.
8) It revealed that "park managers' data specific to the WCNP area
valuable for calibrating MC1 to address other questions about ecosystem
dynamics.." (Symstad, 2017)
Strategic management scenarios-types
This scenario-type approach focuses on resource management
for future forecasting. To reach the goal of this scenario-based planning, we
need to identify the objectives, find competition, evaluate the internal
structure and model, and ensure the C-Level of the organization well
understands the importance of change and future implementations. (Synario,
2021, p. 2) For strategic management scenario-type, we need to be open to
debates, not assuming for the future but measuring things, and avoid biases and
overconfidence about the future.
What if the organization did not do proper scenario-type planning and only
relied on standard forecasting
Bankruptcies, the massive firing of employees, lost
customers, lost reputations, and many other consequences cause not having
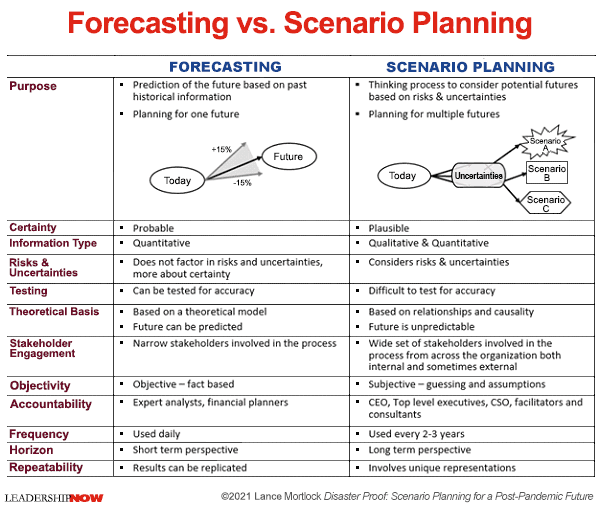
proper scenario-type planning and just relying on the standard forecasting. Fig
2 shows the differences between using scenario-type planning against standard
forecasting of the future. It shows that we can have a plausible prediction of
the future instead of a possible estimation. We can analyze future forecasting
with both Qualitative and Quantitative methods in scenario-type planning
against just Quantitative analysis in regular forecasting of the future.
However, there can be a test for accuracy in the standard forecasting model,
while it is complicated to test the accuracy of predictions in scenario-type
planning. Standard forecasting is subjective-fact-based with a short-term
horizon on an expert analysts' level. At the same time, scenario-type planning
is based on the relationships and causality of events and data and C-Level
perspectives and concerns with a long-term horizon. Lastly, normal forecasting
results can be replicated, while scenario-based planning is a unique
representation. (Leadershipnow, 2021)
References
Al
Saeed, Adeghe, I. J. (2016). Scenario-type Planning. Futuring and
Innovation. Retrieved 2022, from
http://insight-to-the-future.blogspot.com/2016/02/scenario-type-planning.html
CTU,
(2022). Colorado Technical University. Student’s restricted panel.
Retrieved 2022, from Colorado Technical University restricted area of
assignments.
Leadershipnow.
(2021, May 12). Scenario Planning vs. Forecasting: 6 Questions to Ask to
Prepare for a Post-Pandemic Future. Retrieved 2022, from https://www.leadershipnow.com/leadingblog/2021/05/scenario_planning_vs_forecasti.html
Mariton,
J. (2016b). What is Scenario Planning and How to Use It.
Smestrategy.Net. Retrieved 2022, from
https://www.smestrategy.net/blog/what-is-scenario-planning-and-how-to-use-it
Rami,
Luther, A. D. (2020b). Scenario Planning: Strategy, Steps and Practical
Examples. NetSuite. Retrieved 2022, from
https://www.netsuite.com/portal/business-benchmark-brainyard/industries/articles/cfo-central/scenario-planning.shtml
Symstad, A. J.,
Fisichelli, N. A., Miller, B. W., Rowland, E., & Schuurman, G. W. (2017).
Multiple methods for multiple futures: Integrating qualitative scenario
planning and quantitative simulation modeling for natural resource decision
making. In Climate Risk Management (Vol. 17, pp. 78–91). Elsevier BV.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2017.07.002
Synario. (2021,
September 23). Scenario Planning in Strategic Management. Retrieved 2022, from
https://www.synario.com/scenario-planning-in-strategic-management/
Tables & Figures
Fig 1, scenario-type planning work approach (Al Saeed, 2016)
Fig 2, forecasting vs. scenario-type planning (Leadershipnow,
2021)